Bit operations
All numbers in the computer memory are stored in binary form, i.e. as a sequence of 0 and 1.
To store numbers in computer memory, a finite number of digits are used. Because of this, numbers in a computer have a limited range, and the results of calculations may be inaccurate.
An integer can be stored in 8, 16, 32, or 64 bits of memory. Each additional bit expands the range of possible values by 2.
Operations with positive and negative numbers are performed in the processor using the same algorithms.
With the help of bitwise logical operations, you can control individual bits of the registers of the processor and external devices.
| Python operation |
Destination |
a & b |
Bitwise And for a and b |
a | b |
Bitwise OR for a and b |
a ^ b |
X OR for a and b |
~a |
Bit inversion for a |
a << b |
Bitwise shift left of a to b |
a >> b |
Bitwise right shift of a to b |
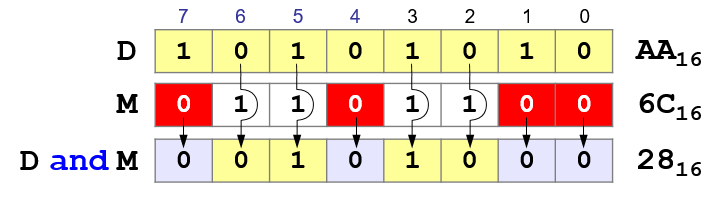
Operation AND
Using the
operation "AND" you can reset (set to zero) bits for which the mask is 0!
Mask – a constant that defines the scope of the logical operation on the bits of a multi-bit number.
D - data,
M - mask
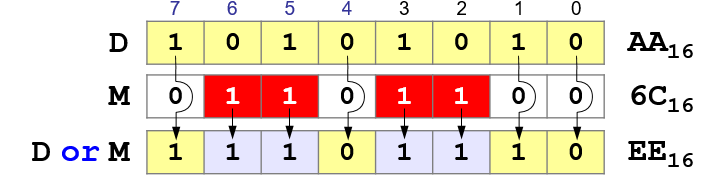
Operation OR
The
operation "OR" can be used to write a 1 to the bits for which the mask is 1!
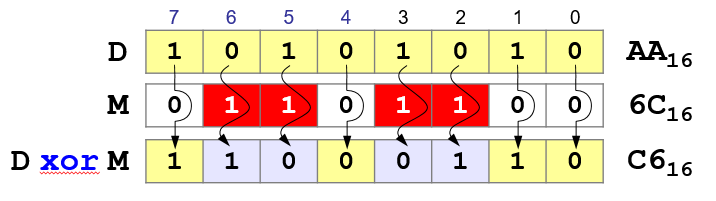
Operation exclusive OR
Using the
operation "XOR" you can invert bits for which the mask is 1!
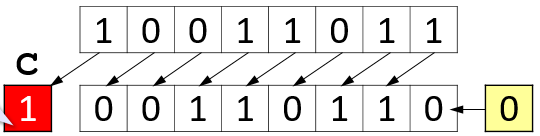
Shift Left
A logical (bitwise)
left shift by 1 bit doubles a positive integer.
Shift Right
Boolean (bitwise) .
shift right by 1 divides a positive integer by 2.
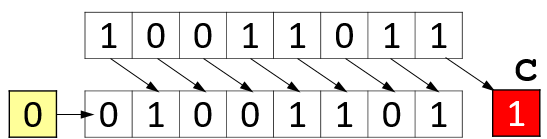
Since a right shift sets the sign bit on the vacated positions, the sign of the number
x can be determined by right-shifting the entire length of the variable.